Introduction to Network Tools
Who am I

- small2kuo 小小郭(胖胖郭)
- NTU CSIE b99
- NA DNS組老人
- SA 退休老人
- FB
Outline
- Network Monitoring/Debugging Tool (user)
- ping, traceroute, mtr, arp, nslookup, dig, host, whois, netcat, netstat
- Networking Setting Tool (administrator)
- ifconfig ifup ifdown route dhclient, ip
- Others Sophisticated Command... (??)
- ssh tunnel, iptables/ufw, tcpdump/wireshark
A little review
- Network System can be analogized to Mail System
- Image this situation...
- 假設台大(subnet)每棟系館(Computer)對外溝通都要透過寄信(Network Packets)
- 每棟系館都有好幾個出入口(interface)
- 每個出入口都有地址(IP address) 是由台大(DHCP server)統一提供的
但實際上每個出入口都有獨立的名稱 是命中註定不可更改的!(MAC address)
- 舉例來說:
- 德田館一號出口 就是個MAC address (也是一個interface)
- 第9020號出口(跟上面指同個地方) 就是個IP address
- 台大擁有對外的地址(public IP):台北市羅斯福路四段一號
- 但是這名字太長了有點難記 所以台大跟台北市地政事務所(DNS server)申請了個Domain name叫做: 台灣大學
- 也就是寄信只要寄到台灣大學(Domain)就知道是寄到台北市羅斯福路四段一號(IP)
Network Monitoring/Debugging Tool (user)
ping
Usage
$ ping <hostname>- send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packets to network hosts
- test connectivity / latency
Example Output
$ ping linux15.csie.ntu.edu.tw PING linux15.csie.ntu.edu.tw (140.112.30.46): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 140.112.30.46: icmp_seq=0 ttl=62 time=1.910 ms 64 bytes from 140.112.30.46: icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=1.950 ms ^C --- linux15.csie.ntu.edu.tw ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0.0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.910/1.930/1.950/0.020 ms
traceroute
Usage
$ traceroute [-p <protocal>] <hostname>- trace packet path in sending direction
- default UDP (can also use ICMP or TCP)
Example Output
$ traceroute linux15 traceroute to linux15.csie.ntu.edu.tw (140.112.30.46), 64 hops max, 52 byte packets 1 10.5.7.254 (10.5.7.254) 1.076 ms 0.809 ms 0.553 ms 2 140.112.16.190 (140.112.16.190) 1.200 ms 1.402 ms 1.273 ms 3 linux15.csie.ntu.edu.tw (140.112.30.46) 1.345 ms 1.178 ms 1.461 ms
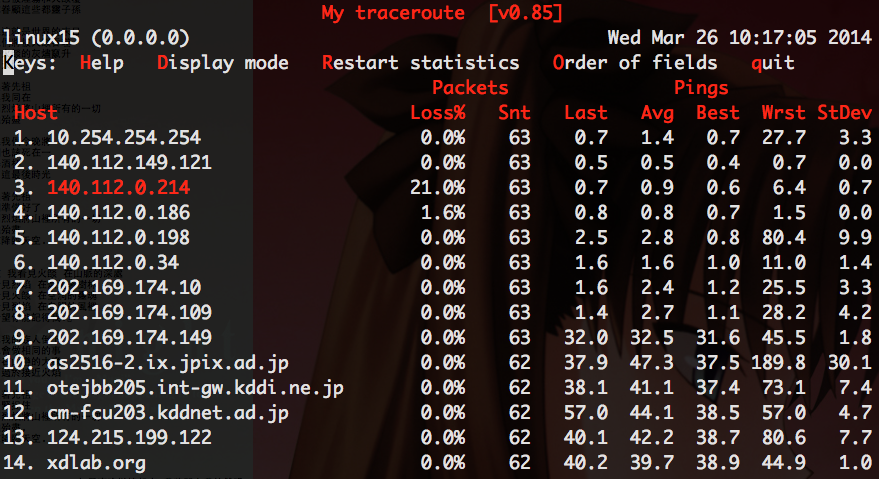
mtr
Usage
$ mtr <hostname>- combinations of ping and traceroute
Example Output
arp
Usage
# linux $ arp [-i if] [-n] [hostname] # mac $ arp [-n] [-a|hostname] # windows $ arp [-a|hostname]- get certain host/all subnet IP => MAC mapping
- can also set hostIP => MAC mapping (administrator)
nslookup/dig/host
- Query for DNS RR Record
nslookupis deprecateddigis more detailed thanhost
Usage
$ nslookup <IP/hostname> [DNS server IP] $ host [-a] <IP/hostname> [DNS server IP] # "host -a" ~= "dig"
dig
$ dig [options] <hostname> [@server]
# +trace trace record since root DNS server
# -t type ANY,A,AAAA,MX,SOA,CNAME...query for certain record
# -x for PTR record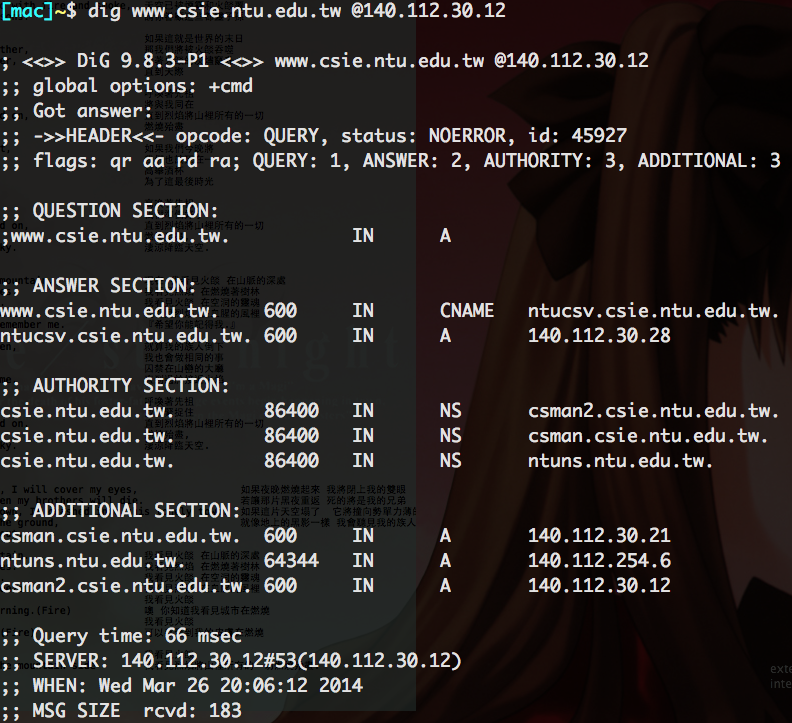
whois
Usage
$ whois <domainname>Query domain and IP registration
netcat, nc
- Usage
client/server model
## Server mode $ nc -l [-u] [-t] [-p <port>] # -l : listening, without -l is client mode (like telnet) ## Client mode $ nc [-u] [-t] [IP|host] [port] # -u : use UDP mode # -t : use TCP mode (default)port scanning
$ nc -z <hostname> <port>-<port>
netstat
Display network connections
$ netstat [-n] [-a] [protocal] [state] [-p] [-c] # -a : all # -p : display running process # -c : continue (dynamic update) # protocal = -t/-u/-w/-x : TCP/UDP/raw/UNIX sockets # state = -l : listening port # -e : active connectionDisplay routing tables (like route)
$ netstat -rDisplay network interfaces
$ netstat -iDisplay interface statistics
$ netstat -s [protocal]
lsof
Usage
$ lsof -i [-n]show process to port (compared to netstat -p)
Networking Setting Tool (administrator)
ifconfig family
- Tool
- NetworkManager (nm)
- ifconfig
- ifup / ifdown
- Purpose
- Show interface configuration
- Configure network interfaces
- Bring up/down interface
- Set IP/netmask
- Add/delete address (alias)
ifconfig
Usage
## Enable setting $ ifconfig <interface> [up|down] ## Create network alias or just assign address to certain interface $ ifconfig <interface> [add|del] <address> [netmask <address>]- Only for temporary use: debugging/system tuning
Default is to show the status of currently active interfaces.
ifup/ifdown
Usage
$ ifup <interface> $ ifdown <interface>- Set the network according to the configuration file
/etc/network/interfaces services networking [start|stop|restart] will callifup/ifdown
/etc/network/interfaces
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 140.112.30.46
netmask 255.255.255.0
network 140.112.30.0
broadcast 140.112.30.255
gateway 140.112.30.254
dns-nameservers 140.112.30.21 140.112.254.4 140.112.2.2
dns-search csie.ntu.edu.twroute (linux)
Usage
## Show table $ route [-n] ## Modify $ route [add|del] [-net <address>|-host <host>] netmask <address> \ [gw <gateway>|dev <Iface>] # ex: route add -net 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.0.254- Show routing table
Manipulate routing table
routing table example
$ route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1000 0 0 eth0
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0- Destination = 0.0.0.0 : default network
- Gateway = 0.0.0.0 : local network
- Routing table is Ordered!!
route (mac)
- Used to modify routing tables
- Cannot show the whole tables!
- Can show a specific route to a certain host.
$ route get <hostname>
# Example
$ route get linux13
route to: linux13.csie.ntu.edu.tw
destination: default
mask: default
gateway: 10.5.7.254
interface: en1
flags: <UP,GATEWAY,DONE,STATIC,PRCLONING>
recvpipe sendpipe ssthresh rtt,msec rttvar hopcount mtu expire
0 0 0 0 0 0 1500 0dhclient
Usage
$ dhclient [-v] [-r] <dev> # -r : release IPExample
$ dhclient -v eth0 DHCPDISCOVER on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 7 DHCPDISCOVER on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 interval 13 DHCPOFFER from 10.0.0.1 DHCPREQUEST on eth0 to 255.255.255.255 port 67 DHCPACK from 10.0.0.1 bound to 10.0.0.100 -- renewal in 791 seconds.
ip
Usage
$ ip [option] [action] [command] # action: link # network device # address # IP/IPv6 # neighbour # ARP # route # routing table- Use
manto help you XD.
More Network Commands....
ssh tunnel (forward tunneling)
Usage
$ ssh [-N -f] -L [local-address:]<local-port>:<remote-host>:<remote-port> <gw> # Example (execute from my laptop): $ ssh -N -f -L 0.0.0.0:8080:google:80 b99@linux15- Connect to remote through gw by local
In this example: I can view
google byhttp://localhost:8080/ onmy laptop throughtlinux15
ssh tunnel (reverse tunneling)
Usage
$ ssh [-N -f] -R [bind_address:]port:host:hostport [user@]hostname # Example (execute from my laptop): $ ssh -N -f -R 0.0.0.0:8080:council:80 b99@ntu- Make me as gw.
In this example: I can view
council byhttp://ntu:8080/ onanywhere throughtmy laptop
tcpdump
- dump traffic on a network
- Display captured packets
- Filter the packets
Example
tcpdump -i eth1 tcpdump -A -i eth0 -w l_1024.pcap tcpdump -n -tttt -i eth0 -r data.pcap less 1024 tcpdump -i -nnvvXXStttts0 eth0 -c 10 -w 08232010.pcap port 22 tcpdump -w xpackets.pcap -i eth0 -s0 'dst 10.181.140.216 and port 22' tcpdump -w comm.pcap -i eth0 -nnvvS 'dst 16.181.170.246 and port 22' tcpdump -i eth0 'not arp and not rarp' tcpdump 'tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn|tcp-fin) != 0 and not src and dst net localnet' tcpdump 'icmp[icmptype] != icmp-echo and icmp[icmptype] != icmp-echoreply' tcpdump 'tcp port 80 and (((ip[2:2] - ((ip[0]&0xf)<<2)) - ((tcp[12]&0xf0)>>2)) != 0)' ...
tcpdump
Usage
$ tcpdump [option] [expression]option
-i <Iface> : Listen on specifiec interfaces.
-n : Don't resolve hostnames.
-nn : Don't resolve hostnames or port names.
-X : Show the packet's contents in both hex and ASCII.
-XX : Same as -X, but also shows the ethernet header.
-v, -vv, -vvv : Increase the amount of packet information you get back.
-s <num> : Define the snaplength (size) of the capture in bytes.
Use -s0 to get everything.
-S : Print absolute sequence numbers.
-e : Get the ethernet header as well.
-q : Show less protocol information.
-c <x> : Only get x number of packets and then stop.
-w <file> : write to pcap file
-r <file> : read from pcap filetcpdump
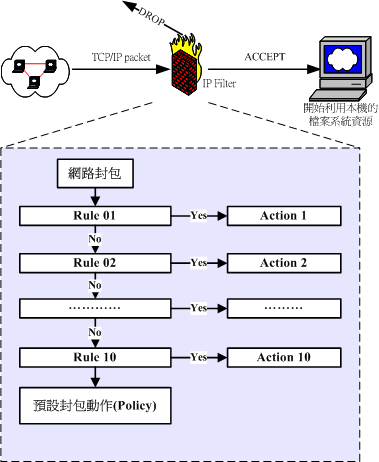
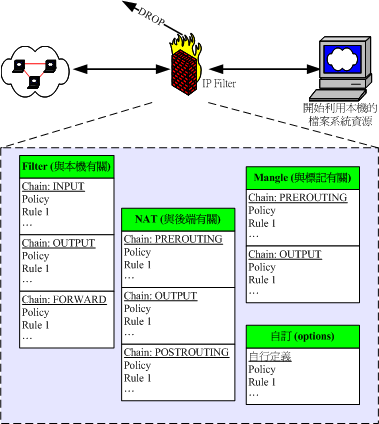
iptables
- Filter
- ACCEPT/DROP/REJECT packets
- Rate limit
- Log traffic
- NAT
- Redirect
- NAT
- Chain, Rule, Policy, Action
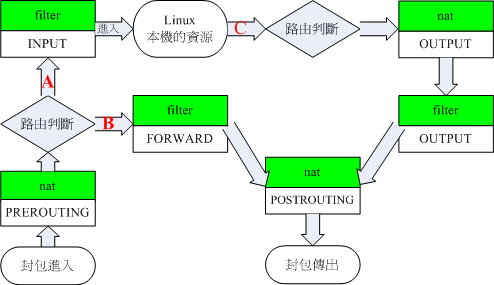
iptables command
$ iptables -t <table> [-F|-X|-Z] [-L] -A <chain>
# -t : filter,nat,mangle,...
# -L : list rules
# -A : INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT,PREROUTING,POSTROUTING,OUTPUT...
# -F : clear rules
# -X : remove user defined table
# -Z : counting and statistics initialize
$ iptables -A <chain> <rule> -j <action>
$ iptables -D <chain> <number>
# action: ACCEPT,DROP,REJECT,LOG,...
# rule: pretty complicated...Orziptables rules
- IPs (-s -d)
- Protocol (-p TCP,UDP,ICMP,...)
- Port (--sport --dport)
- Protocol options
- ICMP type
- TCP SYN/ACK
- etc.
Examples:
$ iptables -A INPUT -i eth1 -s 192.168.100.0/24 -j DROP $ iptables -A INPUT -s 140.112.2.2 --sport 1:1023 -j LOG $ iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 1:1023 --syn -j DROP $ iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT
More and More Command...
- ufw
- socat
- tshark
- iwlist iwconfig wpa_supplicant
- ethtool
- nmap
Homework
Part1
- 簡答題
- 請用linux的command做到以下事情,並將指令與結果記錄(有打星號的)都下來。
- *找出linux15到www.google.com經過了哪些gateway
- *查詢系上mail server的DNS的MX record
- *請用nc送http request到http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw
- *查詢linux15的哪些port正在等待接收(listen)TCP的服務
- 寫出設定網路成以下狀態的指令
- eth0
- IP: 192.168.217.100
- netmask: 255.255.255.0
- gateway: 192.168.217.254
- 擷取送到140.112.172.12且port是23的封包,並同時以hex與ASCII顯示,將結果輸入到out.pcap檔案裡。(不用真的交out.pcap檔案來,也不用記錄螢幕輸出結果)
Part 2
- 情境題
- 假設你筆電是一台linux機器並且上面有跑ssh server(listen port 22)
- 並且你現在系上的內網中10.5.x.x or 192.168.x.x
- 你要怎麼讓在系外的人ssh連到你這台電腦裡
Part 3
- 春假愉快!!
